“The New Europe will be the Middle East”
Mohammad Bin Salman (MBS)
Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia




The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides a positive outlook on the GCC region, highlighting several key economic trends:
- Non-Oil Growth: The IMF notes that non-hydrocarbon growth remains strong across the GCC, driven by increased domestic demand, capital inflows, and reform efforts aimed at diversification. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are making significant progress in expanding sectors such as tourism, technology, and real estate.
- Fiscal Stability: The IMF commends the region’s strong fiscal management, supported by fiscal reforms and high oil prices. Fiscal balances are healthy, with non-oil deficits expected to decrease by 2028 as governments focus on increasing non-oil revenues and controlling expenditures. This is critical for long-term sustainability and economic stability.
- Financial Sector Reforms: The financial sector in the GCC remains robust, supported by continued reforms aimed at enhancing financial stability and deepening capital markets. The IMF encourages further financial sector modernization, including expanding fintech and digital banking.
- Environmental Initiatives: In line with global sustainability goals, the IMF acknowledges the GCC’s environmental reforms, particularly Saudi Arabia’s efforts to reduce carbon intensity and promote renewable energy through projects like NEOM and carbon capture initiatives
Overall, the IMF views the GCC as resilient in the face of global economic uncertainties, with strong growth prospects driven by ongoing economic diversification and fiscal reforms.


The Arab Monetary Fund (AMF) has provided several key insights regarding the economic outlook for the GCC and broader Arab economies:
- Economic Growth: The AMF projects that the overall growth rate for Arab economies in 2023 will slow to around 2.2%, down from 5.8% in 2022, largely due to the tightening of monetary policies and a decline in oil production. However, a recovery is expected in 2024, with growth reaching approximately 3.3%. This rebound is supported by global economic recovery, lower interest rates, and the continued implementation of regional development plans.
- Inflation Trends: Inflation across Arab countries is expected to remain high at 9.3% in 2023 but is projected to decline to around 3.6% in 2024. This decrease will be driven by stabilizing global commodity prices, energy costs, and improved currency exchange stability.
- Policy Recommendations: The AMF highlights the need for Arab countries to continue adjusting fiscal and monetary policies. This includes revisiting subsidy policies, rationalizing tax exemptions, and strengthening social safety nets. They also emphasize the importance of improving the monetary policy framework and implementing macro prudential reforms.
Overall, the AMF underscores the significance of strategic reforms and careful policy management to navigate global economic challenges and enhance long-term growth prospects across the Arab region.
- S&P has given a positive outlook for GCC economies, particularly the banking sector, which it expects to maintain strong profitability due to increased lending, rising fee incomes, and cost efficiencies (Arab News).
- The agency highlights the resilience of GCC countries amid global economic uncertainties, crediting reforms and diversification efforts. For example, Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 has supported growth in non-oil sectors, leading to greater foreign investment and job creation.


- Moody’s expects the GCC economies to grow steadily in 2024, driven by stable oil prices above $80 per barrel, strong non-oil sector growth, and government investments in diversification. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are forecasted to grow by 4.1% and 3.8%, respectively, with inflation easing to 2.3% across the region. Tourism and renewable energy investments, especially in Saudi Arabia, will further boost economic resilience
- Fitch underscores the growth in the GCC debt capital market, which is on track to exceed $1 trillion. The agency sees the region as benefiting from strong government borrowing for infrastructure projects and economic diversification (Forbes ME).
- Fitch has also commended the fiscal strength of GCC countries, particularly Saudi Arabia, for its prudent management of oil revenues and diversification into non-oil sectors like real estate and tourism (TravelDailyNews International) (Forbes ME).


- Goldman Sachs has highlighted the GCC’s strong economic performance, driven by significant investments in non-oil sectors like technology, real estate, and finance. They expect Saudi Arabia and the UAE to continue leading regional growth due to government reforms like Saudi Vision 2030 and the UAE’s focus on becoming a global financial hub.
- Goldman has also noted that the GCC’s sovereign wealth funds are key players in global investment, with increased interest in tech, clean energy, and infrastructure.
- UBS emphasizes the GCC’s role in the global transition to clean energy, with investments in green projects and technology. The bank also points to the region’s strong fiscal policies and economic reforms as key factors driving financial stability
- UBS highlights the real estate sector in Saudi Arabia and the UAE as major areas of interest, with growing property markets that are attracting foreign investment.


- JPMorgan points out that the GCC’s financial markets are becoming increasingly attractive to international investors due to higher oil prices and significant reforms aimed at diversification. The bank sees opportunities in sectors like real estate, banking, and infrastructure, particularly in Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
- The firm also sees GCC governments utilizing oil revenues to fund large-scale projects that are helping to stabilize the region’s economies, despite global uncertainty.
- Morgan Stanley is positive about the GCC’s banking sector, which it believes is well-positioned for future growth. The firm expects higher lending volumes and increased investment in digital banking to support the region’s economic transition.
- They also underscore the importance of the GCC’s sovereign wealth funds, noting their increasing influence on global markets due to investments in tech, infrastructure, and clean energy.

GCC inflation rate since covid



Key factors behind GCC inflation control
Pegged Currencies and Monetary Policies
Most GCC countries peg their currencies to the US dollar, which has helped stabilize inflation by limiting the volatility of their exchange rates. This strategy effectively tied their interest rate policies to that of the US Federal Reserve, allowing them to mirror interest rate hikes and cool domestic inflation. This has been a significant factor in keeping inflation under control across the GCC(PwC)(Global Finance Magazine).
Subsidies and Government Support
GCC countries have maintained subsidies on essential goods like food and fuel, buffering their populations from the global price shocks experienced in other regions. For example, while the UAE liberalized fuel prices, other countries maintained subsidies, which helped manage transportation costs. Additionally, housing rents have become a growing inflationary concern, particularly in places like Saudi Arabia and Dubai, where rent prices have risen steadily. However, food and other consumer goods have seen minimal inflation(PwC)(PwC).
Energy Exports and Revenues
As major oil exporters, the GCC economies benefited from high oil prices post-COVID, allowing governments to cushion their populations through targeted support programs. This energy-driven fiscal strength has enabled them to avoid some of the harsh economic downturns that have fueled inflation in energy-importing countries like the UK and Canada( Global Finance Magazine)(PwC).
Global Supply Chain Impact
While global supply chains were heavily disrupted during and after COVID-19, the GCC's proactive handling of import channels and its relatively smaller population compared to large economies helped mitigate extreme inflation. This contrasts with other regions where supply chain bottlenecks, combined with demand-side pressures, spurred higher inflation( Liberty Street Economics)(Bank of Canada).
Global Supply Chain Impact
While global supply chains were heavily disrupted during and after COVID-19, the GCC's proactive handling of import channels and its relatively smaller population compared to large economies helped mitigate extreme inflation. This contrasts with other regions where supply chain bottlenecks, combined with demand-side pressures, spurred higher inflation( Liberty Street Economics)(Bank of Canada).
Energy Exports and Revenues
As major oil exporters, the GCC economies benefited from high oil prices post-COVID, allowing governments to cushion their populations through targeted support programs. This energy-driven fiscal strength has enabled them to avoid some of the harsh economic downturns that have fueled inflation in energy-importing countries like the UK and Canada( Global Finance Magazine)(PwC).
Comparison with Western Economies
US, UK, Canada: These countries experienced higher inflation, peaking in 2022 due to global supply chain disruptions, energy price shocks (exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine conflict), and labor market pressures. Central banks in these regions responded with aggressive interest rate hikes, which have started to bring inflation down, though the rates remain higher than those in the GCC(Liberty Street Economics)(Bank of Canada).
In summary, the GCC countries' unique economic structure, reliance on energy exports, currency stability, and government support have allowed them to manage post-COVID inflation more effectively than many Western nations.
The key reasons for inflation trends and measures taken by each country:
- Saudi Arabia: The VAT hike in 2020 to 15% helped the country increase its fiscal reserves, stabilizing inflation rates through 2024. Efforts in diversifying the economy and stabilizing oil prices have also been essential in maintaining lower inflation levels.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): After initial deflation in 2020, inflation surged in 2022 due to rising fuel prices and supply chain issues. The UAE has mitigated inflationary pressures through strategic investments in non-oil sectors and the regulation of housing and fuel prices.
- Oman: VAT introduction and budget cuts in 2021 helped control inflation. Despite global challenges, Oman’s efforts in fiscal consolidation and increased hydrocarbon production have kept inflation stable through 2024.
- Kuwait: Rising prices of food and fuel led to increased inflation from 2021 onwards. Kuwait has focused on boosting domestic demand and aligning monetary policy with global trends, resulting in moderate inflation levels by 2024.
- Qatar: Qatar’s inflation spiked post-COVID, driven by VAT increases and heightened demand. The country responded by investing in energy and infrastructure, which helped stabilize inflation by 2024.
- Bahrain: After deflation in 2020, Bahrain raised VAT to 10% to combat deficits, which contributed to moderate inflation through 2024. The country’s fiscal consolidation efforts have played a major role in stabilizing its economy.
These measures reflect how GCC countries have managed inflation by adjusting taxes, regulating prices, and implementing economic reforms following the COVID-19 pandemic.
The typical annual appreciation of property asset in GCC
Dubai








Sharjah




Oman

Apartment Prices
Dropped by more than 17% in Q1 2024.
Villa Prices
Increased slightly by 0.8% in Q1 2024.
Overall Residential Real Estate Prices
Declined across the board, including land.
Regional Price Declines
1. Musandam Region: Largest decline at 15.7%.
2. Muscat: Prices fell by 5.5%.
3. Dhofar Governorate (Salalah): Prices decreased by 5.1%.
Regional Price Declines
1. Musandam Region: Largest decline at 15.7%.
2. Muscat: Prices fell by 5.5%.
3. Dhofar Governorate (Salalah): Prices decreased by 5.1%.
Overall Residential Real Estate Prices
Declined across the board, including land.
Real Estate Sector
1. The sector has been contracting for several months.
2. Analysts consider this trend a temporary "blip."
3. Foreign professionals remain optimistic about future luxury developments.
Leasehold Areas
1. Data reflects trends mainly in leasehold areas (foreigners control property for up to 99 years).
2. May not offer a complete picture of the real estate market.
Freehold Areas
1. Foreigners fully own property rights.
2. Areas like Yiti, Muscat Bay, and Jebel Sifah saw a 12% price increase from June 2023 to June 2024.
3. These areas are still under construction.
4. The 3% registration fee is not yet applicable, contributing to incomplete data recording.
The typical annual rental yield of property asset in GCC


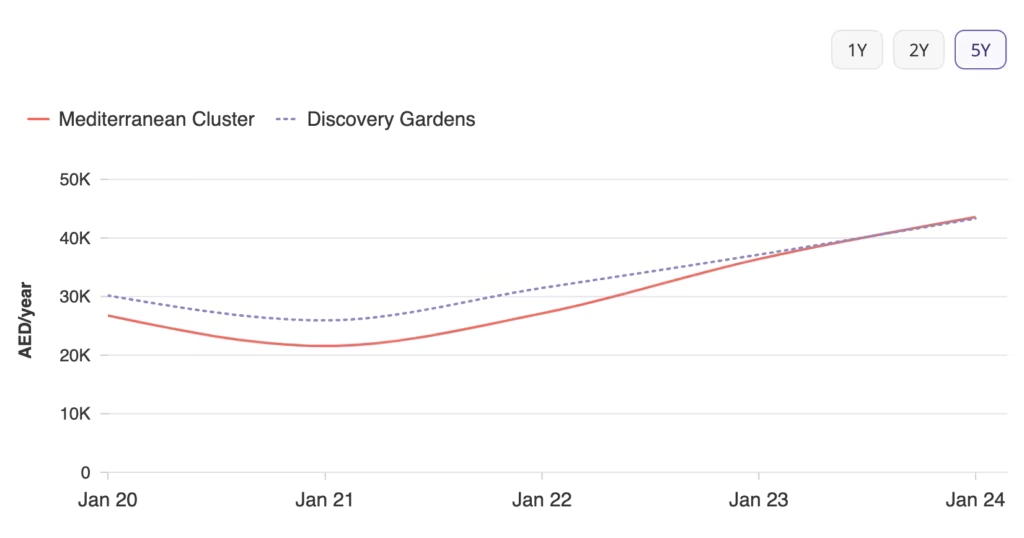




The growth of Uae, Oman and Ksa markets



Top attractions for investors to invest in GCC
Dubai
- 3-5 years
- Dubai Hills Estate
- Jumeirah
- Mina Rashid
- JLT
- Al Furjan
- Damac Hills
- 5-7 years
- Dubai South
- Dubai Silicon Oasis
- Palm Jabel Ali
Sharjah
- 3-5 years
- Aljada
- Sharjah Waterfront City
- Maryam Island
- Masaar
- Hayyan
- Sharjah Sustainable City
Oman
- 3-5 years
- Sultan Haitam City
- Sustainable City
- Muscat Bay
- 5-7 years
- Maysan Square Duqm
- Aida
- Uptown KOM Muscat
Saudi Arabia
- Real Estate Laws are still being updated for foreign investors
- Digitalization is in progress
- Once the local expat population becomes acquainted with the new system, it will be an excellent time to invest.
- Minimum $1.1million investment is required.
Real Estate Analyst Opinions
Uae
- Customer preferences in the UAE residential real estate market lean towards luxury, high-end properties, including spacious villas and apartments with modern amenities and prime locations, such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
- Key market trends:
- Sustainable properties are in demand, with buyers seeking energy-efficient homes that incorporate green technologies like solar panels and water-saving fixtures.
- Off-plan properties (sold before completion) are increasingly popular, attracting investors with lower prices and potential for value appreciation.
- Local factors:
- A large expatriate population creates high demand for rental properties in popular expat communities, where landlords achieve high rental yields.
- Government regulations protect both landlords and tenants, ensuring a stable rental market.
- Macroeconomic factors:
- A strong, diversified economy driven by oil, tourism, and finance is supporting population growth and real estate demand.
- Favorable policies for foreign buyers, including property ownership in designated areas and long-term residency visas, boost investment in the market.
- Customer preferences in Oman’s residential real estate market are shifting towards properties with modern amenities and a luxurious lifestyle, such as gated communities featuring pools, gyms, and recreational areas. Additionally, there is a rising demand for energy-efficient and sustainable properties.
- Market trends:
- Off-plan properties are growing in popularity due to lower prices and customizable options. Developers offer attractive payment plans and incentives to draw buyers.
- The rise of integrated communities that provide amenities like schools, shopping centers, and healthcare facilities in one development is also gaining traction.
- Local factors:
- A growing population and government policies, such as the relaxation of foreign ownership restrictions, have increased demand for residential properties, especially among foreign investors and expatriates.
- Macroeconomic factors:
- Oman’s stable economy, with low inflation and growing GDP, supports the real estate market’s development. Additionally, infrastructure investments in roads and airports have improved accessibility, creating a favorable climate for both local and international investors.
Oman
Saudi Arabia
- Customer preferences in Saudi Arabia’s residential real estate market are shifting towards larger, more luxurious properties due to rising wealth and disposable income. Buyers are particularly drawn to spacious homes with amenities like swimming pools, gyms, and green spaces.
- Market trends:
- High-rise buildings and gated communities are on the rise, reflecting the need to accommodate a growing population and the desire for secure, exclusive living environments.
- Local factors:
- Government initiatives, such as mortgage laws and the establishment of real estate financing companies, have made property purchases more accessible.
- Infrastructure and transportation investments have further stimulated the real estate market.
- Macroeconomic factors:
- Saudi Arabia’s economic growth, driven by increased oil prices and diversification efforts, has boosted employment and income, contributing to higher demand for residential properties.
- Low interest rates have also made it more affordable for individuals to borrow and invest in real estate.
In conclusion, Saudi Arabia’s residential real estate market is rapidly growing due to changing preferences, government policies, and strong economic fundamentals, with expectations for continued expansion in luxury property demand.



